약물전달시스템 기반의 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단 나노입자(나노겔)를 이용한 노화 방지 화장품 개발
Development of Anti-aging Cosmetics Using Chitosan/ γ-Cyclodextrin/Fucoidan Nanoparticles (Nanogel) Based on the Drug Delivery System
利用基于给药系统的壳聚糖/γ-环糊精/岩藻多糖纳米颗粒(纳米凝胶)开发抗衰老化妆品
Article information
Abstract
목적
본 연구는 DDS System을 기반한 감마사이클로덱스트린/키토산/후코이단 나노 입자( CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel))를 포함한 화장품 원료인 MARINAVI-FD를 개발하고 항산화와 보습의 유효성을 입증한 안티에이징 화장품 개발에 목적이 있다.
방법
생분해성 저분자 키토산, 저분자 후코이단, γ-사이클로덱스트린을 혼합한 나노 입자를 확인하고 사이즈와 분포도 측정을 위해 전자현미경(SEM) 분석과 나노입도분석(DLS)를 통해 확인하였고, CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)의 in-vitro 유효성 평가를 위해 DPPH와 ABTS를 통해 확인하였다. 피부각질세포(HaCaT cell)의 MTT assay을 통해 세포생존율을 확인하였고 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay을 통한 보습 효능을 확인하였다. 화장품의 소재 적용을 위해 MARINAVI-FD로 원료화 하여 화장품을 제조하였고, 4℃, 25℃, 45℃, 60℃의 온도 조건에서 1, 2, 4, 12 주 기간으로 pH의 변화와 분리 및 침전, 변색, 변취를 확인하였다. 인체적용시험은 사용 전, 사용 2주 및 4주 후에 Moisture D compact 기기 측정을 진행하였다.
결과
나노입자는 대략 500 nm 부근의 분포도와 나노입자가 안정하게 되었음을 확인하였다. 항산화 효능에서는 DPPH 결과는 후코이단에 비해 CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)의 DPPH radical 소거능이 모든 처리 농도에서 더 높게 나타났다. ABTS 결과, 후코이단 보다 H-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel) 의 ABTS radical 소거능이 더 높게 확인되었다. 피부각질세포(HaCaT cell)에서 H-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)은 5,000 μg/mL 의 농도까지 80%이상의 생존률을 보였다. Hyaluronic acid (HA) 생성량을 측정한 결과 대조군 200 μg/mL의 농도에서 121.47 ng/mL HA 생성량에 비해 H-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)이 194.87 ng/mL으로 더 높은 HA 생성량을 보였다. 안티에이징 화장품의 각 온도 조건과 일정 기간 동안 스킨과 크림 제형의 안정성을 확인하였다. 피부 인체적용시험을 통한 피부 2.5 mm 깊이의 보습 효과 결과는 사용 전에 비해 4주 후 시점에서 사용 전에 비해 유의미하게 개선됨을 확인하였다.
결론
본 연구에서는 감마사이클로덱스트린/키토산/후코이단 나노입자; CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)를 활용하여 이를 포함한 MARINAVI-FD 소재화하여 안티에이징 화장품 개발에 있으며 이는 보다 효율적으로 후코이단을 피부에 안정적으로 유효성을 전달하여 피부의 2.5 mm 깊이에서 보습 효과를 입증하였다. 또한 MARINAVI-FD는 특정 제형에 한정하지 않고 안전하게 사용할 수 있는 원료임을 시사 한다.
Trans Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to develop MARINAVI-FD, a cosmetic material containing γ-cyclodextrin/chitosan/fucoidan nanoparticles, i.e., CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel) based on the DDS system, and anti-aging cosmetics that have proven antioxidant and moisturizing effects.
Methods
CH-γ-CD-Fu (nanogel) was identified through electron microscope (scanning electron microscope) analysis and nanoparticle size analysis (dynamic light scattering). Radical scavenging DPPH and ABTS assays were performed. Skin keratinocytes (HaCat cells) was assessed by the MTT assay, and the moisturizing effect was evaluated through enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Temperature and storage conditions were checked for the stability of the formulation. In the human body application test, Moisture Meter D Compact device was used.
Results
The CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel) has confirmed particle size of approximately 500 nm. In the DPPH and ABTS assays, compared with Fu (foucoidan), the CH-γ-CD-Fu (nanogel) showed higher scavenging ability at treatment concentration of 15.625–500 μg/mL. CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel) showed a survival rate of >80% in skin keratinocytes (HaCat cells) up to a concentration of 5,000 μg/mL. In the measurement of hyaluronic acid production, CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel) showed better production at 194.87 ng/mL than at 121.47 ng/mL at a concentration of 200 μg/mL in the control group. The stability of skin and cream formulations of anti-aging cosmetics containing MARINAVI-FD was confirmed. The moisturizing effect was observed 2.5 mm depth of skin human application.
Conclusion
In this study, CH-γ-CD-Fu (nanogel) was used to materialize into anti-aging cosmetics.
Trans Abstract
目的
本研究旨在开发基于DDS系统的含有γ-环糊精/壳聚糖/岩藻多糖纳米粒子即CH-γ-CD-Fu(纳米凝胶)的化妆品材料MARINAVI-FD,证明其抗氧化和保湿作用为开发抗衰老化妆品。
方法
通过电子显微镜(扫描电子显微镜)分析和纳米粒径分析(动态光散射)对CH-γ-CD-Fu(纳米凝胶)进行鉴定。进行了自由基清除DPPH和ABTS 测定。通过MTT法评估皮肤角质形成细胞(HaCat细胞),通过酶联免疫吸附法评估保湿效果。检查温度和储存条件以确定制剂的稳定性。在人体应用测试中,使用了Moisture Meter D Compact装置。
结果
CH-γ-CD-Fu(纳米凝胶)已确认粒径约为 500 nm。在DPPH和ABTS测定中,与foucoidan相比,CH-γ-CD-Fu(纳米凝胶)在处理浓度15.625-500 μg/mL时表现出更高的清除能力。 CH-γ-CD-Fu(纳米凝胶)在浓度高达5,000 μg/mL 的皮肤角质形成细胞(HaCaT 细胞)中显示出 >80% 的存活率。在透明质酸产量的测量中,CH-γ-CD-Fu(纳米凝胶)在浓度为200 μg/mL 时,其产量为 194.87 ng/mL,高于对照组的 121.47 ng/mL。含有MARINAVI-FD 的抗衰老化妆品的皮肤和霜配方的稳定性得到了证实。在人体皮肤2.5毫米深度处观察其保湿效果。
结论
本研究将CH-γ-CD-Fu(纳米凝胶)用于抗衰老化妆品。
Introduction
최근 화장품 시장에서는 유효성분을 직접적으로 피부에 흡수시키는 경피 약물 전달 시스템(trans dermal drug delivery system, TDDS) 기술을 활용하여 코스메슈티컬 시장에 기술을 선보이고 있다. 또한 안티에이징 화장품에 이와 같은 기술을 융합하여 피부의 손상된 세포를 찾아 빠르고 정확하게 흡수되도록 의약품에 쓰이는 약물전달시스템(drug delivery system)에서 화장품으로 응용되어 기업 중심으로 소재 개발에 경쟁력을 높이고 있다(Zhang et al.,2023).
수산 자원의 다당류, 효소, 지질, 단백질 등은 바이오 산업에서 중요한 역할을 한다. 특히 해조류 유래 다당류는 세포벽의 구조적 구성 요소를 포함하며 알긴산, 후코이단, 카라기난 등이 있다(Anisha et al.,2022). 후코이단은 항산화, 항균, 비만방지, 항알레르기, 항암, 항균, 항바이러스, 항응고제 및 항종양 특성에 기초하여 다양한 의 약 및 생물학적 용도의 사용이 증가하고 있다(Cunha et al., 2016). 후코이단은 다양한 제약제제 기술을 사용할 수 있는 몇 가지 물리적인 특징을 갖는데 점액 접착, pH 온도 및 효소 반응이 포함된다. 후코이단은 많은 화합물과 고분자와 결합하는 강한 능력을 가지고 있다. 결합 친화력은 주로 음전하 표면의 성질을 가지고 있다. 후코이단을 반대 전하와 섞게 되면 폴리머, 겔화, 메트릭스와 필름을 형성하는 특징을 가지고 있다(Haggag et al., 2023). 후코이단은 나노입자 제형의 다양한 생물 의학응용을 위한 나노 기술 기반에서 핵심적인 역할을 하고 있으며 나노 의학에서 자체적으로 효과적인 치료제로 사용되는 것 외에도 많은 약물의 나노 운반체로 사용되거나 다른 양이온 폴리머와 결합하여 나노캡슐화 할 수 있다(Zayed et al., 2022). 사이클로덱스트린은 친수성 외부 표면과 친유성 중앙으로 비어 있는 도넛모양을 한 구조물로 glucose 분자가 6개로 결합된 α-CD, 7 개인 β-CD, 8개인 γ-CD로 3가지 종류가 있다(Singh et al., 2002). 이러한 CD의 내부는 C-H와 글루코시드 산소만이 존재하여 소수성(hydrophobic)을 나타낸다. 각종 소수성 화합물인 guest 물질을 포접시켜 복합체를 형성할 수 있다(Lee et al., 2014). CD가 다양한 유기 분자와 복합체를 형성하는 능력과 잘 용해되지 않는 약물을 용해시키는 능력은 이미 잘 확립되어 있으며, CD를 포함하는 Nanogel은 Drug Delivery System에서 유용 성분을 전달하는 생물 의약 분야의 유망 하다(Maria et al., 2012). 후코이단의 나노입자 기반 치료법은 제약업계에서 많은 관심을 받고 있으며 마이크로파, 에멀젼, 용매증발, 그린합성, 고분자 자기조립, 침전, 초음파법 등을 이용하여 합성되어 왔다(Venkatesan et al., 2022).
키토산은 친수성이며 이온 교환기로서 효율성에 기여하는 많은 아미노기를 갖는 생체 고분자이며 이온 흡착제로 알려져 있다(Jha et al., 1988). γ-CD 은 유기, 무기 분자와 결합할 수 있어서 많이 알려져 있으며 이상적인 결합 부위를 가지고 있다(Ikeda et al., 2002). γ-CD를 키토산과 혼합하면 더 나은 흡착 특성을 가진 생체 적합성 물질을 이루며 다른 물질과의 결합 효율 또한 향상시킬 수 있다(Mishra et al., 2011). 안정성, 용해도 및 세포막 투과성을 높이기 위해 알긴산염, 셀룰로오스 유도체, 사이클로 덱스트린(CD) 및 리포좀과 같은 다양한 중합체 나노 캐리어를 사용한 약물 전달이 연구되어 왔다(Fülöp et al., 2015).
키토산의 나노입자 내에 커큐민을 함유한 사이클로덱스트린의 형성의 구조에서는 커큐민을 포획하여 봉입한 사이클로덱스트린 입자는 수용성 이 향상되어 장기간 방출을 통해 키토산으로 캡슐화 할 수 있음을 확인하였다(Karpkird et al., 2020).
바이오기술 및 나노기술을 화장품 산업에 도입하여 미용 목적에 부합하는 생체안전성 유효 성분이 피부 진피층으로 전달하기 위한 시도와 저분자량 펩티드, 핵산, 마이셀, 리포솜, 줄기세포, 경피흡수 촉진 기술을 활용한 기능성 화장품의 전망이 높다(An et al., 2023).
본 연구는 DDS System을 기반한 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단 나노 입자를 CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)이라 명칭하고 이것을 포함한 화장품 원료인 MARINAVI-FD를 개발하고 항산화와 보습의 유효성을 입증한 안티에이징 화장품 개발에 목적이 있다.
Methods
1. 후코이단 추출
다시마는 ㈜바다품애 (Korea)에서 완도산을 구입하였으며 5-6회 수세 및 중금속 제거 후 건조하였다. 분쇄하여 파우더화 하여 냉동 보관하여 사용하였다.
추출 방법은 Lee et al. (2018)을 응용한 방법에 따라 추출하였으며, 다시마 분말 25 g에 4배의 aceton (Sigma-Aldrich, USA)을 가하여 24 h간 동안 실온에서 추출한 뒤 8000×g, 4℃, 15 min 동안 원심분리기로 상층액은 분리하였다. 침전물에 다시 aceton을 동일한 양으로 가하여 12 h 동안 방치하였다. 12 h 후 같은 조건으로 원심분리기로 상층액을 분리하였다. 침전물에 증류수 500 mL를 가하여 40℃에서 24 h 동안 추출하여 여과지(Whatman®Filter Papers No. 2; GE healthcare Life Sciences, UK) 로 여과한 후 여과액을 rotary vacuum evaporator (EYELA N-1000; Tokyo Rikakikai Co., Japan)를 사용하여 60℃에서 감압 농축하였다. 침전물을 증류수 500 mL에 0.05 M Zinc sulfate (Sigma-Aldrich) 25 mL, 0.3 N barium hydroxide (Sigma-Aldrich) 25 mL을 섞은 용액에서 60℃, 3 h 동안 추출하였다. 4℃에서 5,000×g로 10 min 동안 원심 분리하여 얻은 상층액을 rotary vacuum evaporator (EYELA N-1000; Tokyo Rikakikai Co., Japan)로 감압 농축하여 동결 건조기(PVTFA 10AT; ILSIN, Korea)를 이용하여 동결 건조한 후 얻은 후코이단 파우더를 냉 보관하여 실험에 사용하였다.
2. CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel) 제조
Chitosan (50KDa-190KDa, Low molecular, Sigma-Aldrich)과 γ-cyclodextrin (1297.14 mM, Sigma-Aldrich)을 사용하였으며 γ-Cyclodextrin 15 g을 3차 증류수 100 mL에 첨가하여 교반하여 녹여 준 뒤 Chitosan을 0.1% acetic acid 에 탈아세틸화 시켜 녹여준 뒤 2.5 g을 첨가한다. 후코이단 200 mg을 추가하여 24 h 동안 교반한 후 이온복합체의 균일한 나노입자 형성을 위해 3 h 동안 40℃에서 Sonicator (VCX500; Sonics & Materias, Inc., USA)을 60 MHz로 20 min 간격으로 초음파 처리하였다. 냉장 보관 후 나노 분산을 위해 High pressure homogenizer (MN600P-200; MICRONOX, Korea)을 15,000 psi 조건에서 3회 이상 통과하였다.
3. CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)의 입도 분포도 분석과 형태 확인
1) 제조된 나노 입자의 입도 분포는 Zeta Potential (ELS-Z; Photal Otsuka Electronics Inc., Japan) 로 측정하였다. 분석용 시료는 에탄올 1%에 용해하여 사용하였다.
2) 나노 입자의 형성을 확인하기 위해 SEM (S-4800; Hitachi, Japan) 장비를 활용하였다. 입자크기는 나노미터에서 마이크로미터까지 다양하게 확인할 수 있다(Liu et al., 2023).
4. CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)의 항산화 효과 측정
1) 전자공여능 측정
전자공여작용(electron donating abilities, EDA)은 Blois (1958)의 방법을 변형하여 사용하였다. 1 Mm DPPH 용액 100 μL 과 nanogel (15.625-500 μg/mL)을 100 μL씩 취하여 혼합한 후 30 min 동안 암실에서 방치한 후 남아 있는 radical 농도를 Microplate Reader (iMark; BIO-RAD, USA)를 이용하여 517 nm에서 측정하였다. 활성비교를 위해 항산화 물질로 잘 알려진 ascorbic acid, BHT와 비교하였다. 전자공여능은 시료첨가군과 무첨가군의 흡광도 차이를 백분율로 나타내었다.
2) ABTS radical 소거활성 측정
2,2'-azinobis-(3-ethyl-benzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid (ABTS) 와 potassium persulfate를 혼합하여 암소에 두면 ABTS 라디칼이 생성되는데 추출물의 항산화 물질과 반응하여 양이온이 소거됨으로써 특유의 청록색이 탈색되며 이의 흡광도를 측정하여 항산화 능력을 측정할 수 있다. 시험 용액은 증류수에 7 mM ABTS와 2.45 mM potassium persulfate를 첨가하여 상온에서 16 h 배양하여 ABTS 양이온을 생성시킨 후 734 nm에서 흡광도의 값이 0.7 이하가 되도록 희석하여 제조하였다. 그 다음 ABTS 용액 100 μL에 시료 용액 100 μL를 가한 후 6 min 후에 흡광도를 측정하였다. 활성 비교를 위하여 항산화 물질로 잘 알려진 ascorbic acid, BHT와 비교하였다. 음성대조군(2.45 mM potassium persulfate buffer)의 흡광도와 비교하여 흡광도를 감소시키는 정도를 %로 나타내었다(Kim et al., 2019).
5. CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)의 보습 효과 측정
1) 세포 배양
HaCaT 세포는 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco, USA)과 1% antibiotic-antimycotic (Gibco)이 첨가된 Dulbecco's Modified Essential Medium (DMEM, Gibco)을 사용하여 37℃, 5% CO2 조건이 유지되는 배양기에서 배양하였다. Trypsin-EDTA (Gibco)를 이용하여 2-3일에 한 번씩 계대 배양하여 실험에 사용하였다.
2) 세포 독성 평가
HaCaT 세포를 96-well plate에 1×104 cells/well 농도로 분주한 후 배양하였다. 24시간 후 시료를 DMEM에 희석하여 처리한 후 다시 24 h 동안 배양하였다. 그 후, 배지를 제거하고 0.5 mg/mL 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT; Sigma-Aldrich)용액 100 μL를 처리한 뒤 10 min 동안 배양기에서 배양하였다. 이후 MTT 용액이 포함된 배지를 제거하고 생성된 formazan을 DMSO를 이용해 녹인 다음 510 nm에서 microplate reader (Molecular Devices, USA)를 이용하여 흡광도를 측정하였다.
3) Hyaluronic acid (HA) 생성량 측정
HaCaT 세포를 24 well plate에 1×104 cells/well의 농도로 분주하여 배양한 후, FBS가 첨가되지 않은 DMEM로 교체하여 18 h starvation 하였다. 각 시료를 농도별로 희석하여 처리하고 24 h 동안 배양하였다. 배양된 세포의 배지를 회수한 후 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Abcam, UK)를 이용하여 제조사의 매뉴얼에 따라 수행한 후 측정하였다. Hyaluronic acid의 생성량은 제조사에서 제공한 standard protein을 통해 작성된 표준 곡선을 이용하여 나타내었다.
6. 안티에이징 화장품 개발
1) CH-γ-CD-Fu (nanogel)의 화장품 원료화
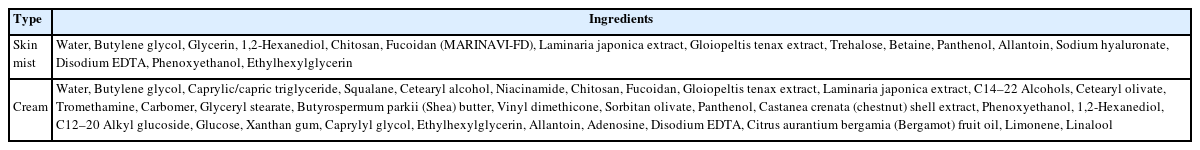
대한화장품성분사전 상품명 MARINAVI-FD 등재
2) MARINAVI-FD를 함유한 안티에이징 기초 화장품 제조
스킨(미스트) 제형은 50℃에서 수상의 원료를 베이스로 두고 재료를 추가하여 Agi-mixer (1500-2000 rpm)으로 교반하면서 서서히 상온으로 유지 교반한다. MARINAVI-FD는 0.5-2% 이내로 포함한다. 크림 제형은 O/W 타입으로 수상의 베이스 80℃로 준비하고 유상의 원료 80℃ 베이스 녹은 뒤 Homo-mixer 2500 rpm에서 혼합하여 유화시켜 준다. 20 min 동안 혼합하여 주고 40℃ 이하에서 첨가물을 투입한 후 5 min 더 교반 후 냉각한다. MARINAVI-FD는 0.8-2.5% 이내로 포함한다.
3) 안티에이징 화장품의 안정성 평가
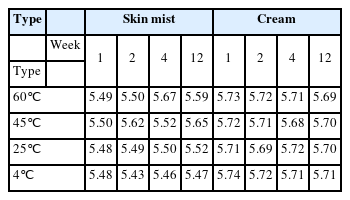
온도의 조건 4℃, 25℃, 45℃, 60℃에서 1주, 2주, 4주, 12주 기간으로 pH의 변화와 분리 및 침전, 변색, 변취를 확인하였다. 안정성테스트의 온도와 기간 설정은 식품의약품안전처 화장품 안정성 시험 가이드라인에 따라 설정하였다. pH 측정은 pH meter 440 (Corning, USA)을 이용하였다.
7. 피부 2.5 mm 보습 개선 효과 인체적용시험
CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)을 1% 이상 함유한 Marinavi-FD 성분의 피부에서의 효능을 알아보기 위해서 헬싱키 선언에 근거한 윤리규정, 식품의약품안전처 인체적용시험가이드에 따라 수행되었으며, 보건복지부의 생명윤리 및 안전에 관한 법률에 따라 (재)한국화학융합시험연구원 헬스케어 연구소 피부과학임상센터에 의뢰 건강한 피부를 가진 만 20-59세 이하의 성인 여성 22명을 대상자로 2023년 5월 16일부터 2023년 6월 12일까지 인체적용시험을 실시하였다(KTRHR-23-0014). 피험자들의 안면부 왼편에 단순 후코이단이 함유된 Marinavi-Basic (마리나비 베이직)과 안면부 오른편에 키토산/감마사이클로 덱스트린 /후코이단(Nanogel)을 포함한 Marinavi-FD(마리나비-에프디)를 사용하였고 피부 2.5 mm 보습 개선효과를 확인하기 위해 안면부에 사용 전, 사용 2주 및 4주 후에 Moisture D compact (Delfin Technologies Ltd., Finland)을 이용하여 측정하였다.
8. 통계분석 방법
본 실험에 사용한 측정값은 3회 이상 반복하여 평균값으로 나타내었으며, 통계학적 유의성은 통계학적 유의성은 Student's t-test로 분석하였으며, p value가 0.05 미만일 경우 통계적으로 유의한 것으로 판정하였다(*p<0.05; **p<0.01).
Results and Discussion
1. CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)의 입도 분포도 분석과 형태 확인
CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel) 제조하여 그 입자를 측정한 결과, 대략 10%의 크기가 큰 입자를 제외하고 입자 분포의 평균 입도가 약 513.85 nm로 확인할 수 있었다(Figure 1A). 효율적인 경피 흡수 촉진 요인으로 나노 입자 평균이 약 500 nm 부근인 것을 감안하면(Chung & Han, 2014) 양호한 나노 입자가 확인되었다. 또한 전자 현미경 촬영 결과 안정화된 나노 입자가 확인되었다(Figure 1B). Cyclodextrin 의 101-103 의 approx. diameter (nm)의 입자의 크기가 Nanogel이며 liposome의 크기 정의와 동일하며, Nanogel은 유용 성분을 포함하고 보호할 수 있으며 고친화성 작용기와 외부 자극에 반응하는 형태이며 생분해성 결합을 통해 유용성분의 방출을 조절할 수 있는 입자의 크기로 본다(Maria et al., 2012). 키토산과 후코이단의 나노복합체는 구립형태를 나타내기 때문에(Kim et al., 2022) 입자 형성은 안정한 것이라 할 수 있다. Liu et al. (2022) 연구에 따르면 후코이단은 자체 전하로 인한 상호 작용을 통해 입자를 안정화 할 수 있기 때문에 안정한 구립 형태의 결과라고 할 수 있다.
2. CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)의 항산화 효과 측정
1) 전자공여능
키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단(Nanogel)은 14.57, 29.14, 47.39, 53.71, 59.74, 65.89% 소거능이, 후코이단은 7.52, 12.14, 24.75, 31.95, 35.73, 39.42%의 소거능이 확인되었다. 양성대조군으로 사용된 BHT의 경우 12.08, 26.32, 32.36, 56.49, 75.31, 84.38%로 확인되었다(Figure 2A). 후코이단 단독보다는 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단의 DPPH radical 소거능이 더 높게 확인되었으며 나노입자가 항산화력 촉진에 도움을 줘서 이러한 결과를 나타낸 것으로 사료된다. 또한 양성대조군 BHT와는 125 μg/mL 농도에서 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단의 소거능이 비슷하게 나타났다. Lee et al. (2021)에서도 대표적인 항산화 물질의 양성대조군과 비교하여 결과가 유의미함을 확인하였다.
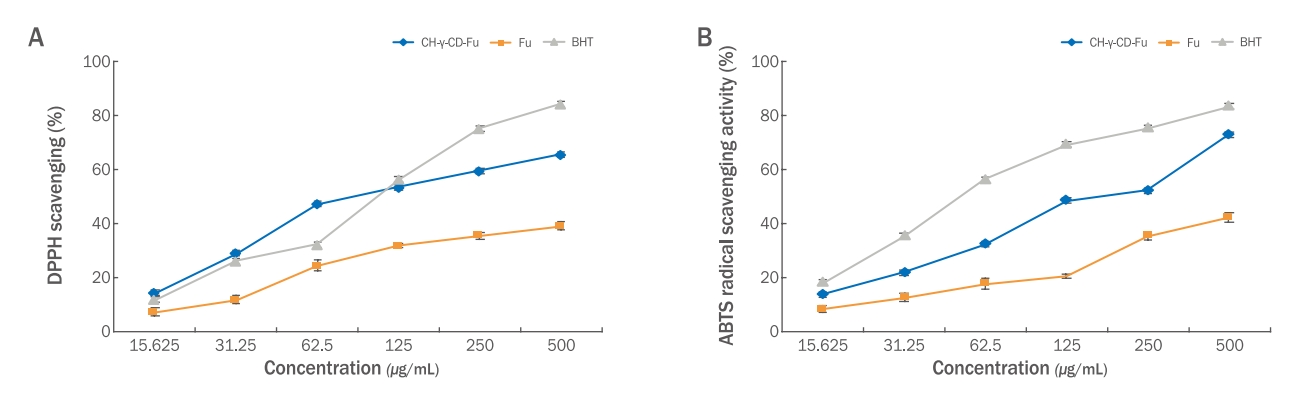
Evaluation of the antioxidant efficacy of CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel).
(A) DPPH radical scavenging assays were conducted to investigate the antioxidant effect of CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel) and fucoidan at varying concentrations: 15.625, 31.25, 62.5, 125, 250, and 500 µ/mL. Data are represented as mean±standard deviation. (B) ABTS radical scavenging assays were conducted to investigate the antioxidant effect of CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel) and fucoidan at varying concentrations: 15.625, 31.25, 62.5, 125, 250, and 500 µ/mL. Data are represented as mean±standard deviation.
2) ABTS radical 소거활성
키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단(Nanogel)과 후코이단의 ABTS radical소거능을 측정한 결과, 키토산/감마-사이클로 덱스트린 /후코이단(Nanogel)은 13.6, 21.89, 32.14, 48.42, 52.16, 72.9% 소거능이, 후코이단은 8.2, 12.45, 17.5, 20.25, 35.25, 42.12%의 소거능이 확인되었다. 양성대조군으로 사용된 BHT의 경우 18.08, 35.22, 56.26, 69.19, 75.21, 83.28%로 확인되었다(Figure 2B). 대표적인 항산화 물질의 양성대조군과 비교하여 결과가 유의미함을 나타낸다(Um & Ryu, 2022). 후코이단 단독보다는 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단의 ABTS radical 소거능이 더 높게 확인되었으며 나노 입자가 더 빠른 항산화 반응을 일으키는 것으로 사료된다.
3.CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)의 보습 효과 측정
1) 세포 독성 평가
HaCaT 세포에 대한 시료의 세포독성을 확인하기 위해 농도별로 24 h 동안 처리하고 MTT assay를 통해 세포독성을 평가하였다. 시료를 300, 500, 700, 1,000, 3,000, 5,000 μg/mL의 농도로 24 h 동안 처리한 결과, Figure 3A에서 보여주는 바와 같이 농도별로 대조군은 104.41, 104.68, 105.06, 100.66, 94.60, 84.93%, 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단(Nanogel)은 92.08, 86.93, 89.02, 85.19, 86.44, 80.37%, 후코이단은 103.27, 106.30, 107.72, 94.93, 93.66, 86.42%의 생존율을 나타냈다.
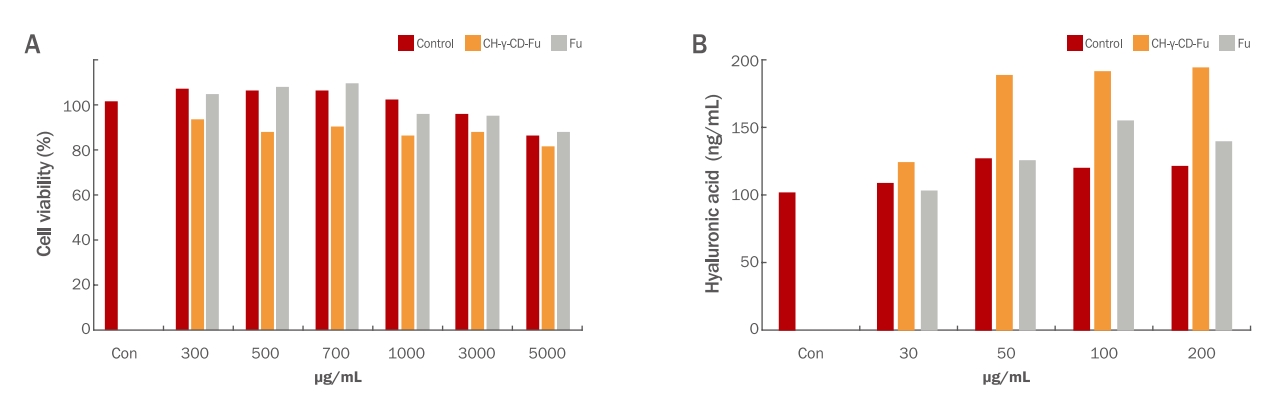
Evaluation of the moisturizing effect of CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel).
(A) Effect of the extract on the viability of HaCaT cells. Cells were treated with different concentrations, i.e., 0, 300, 500, 700, 1000, 3,000, and 5,000 μg/mL, for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by the MTT assay as described in the Materials and Methods. The results are expressed as means±standard deviations of three independent experiments. (B) Effect of the extract on the production of hyaluronic acid in HaCaT cells. Cells were treated with sample concentrations of 0, 30, 50, 100, and 200 for 24 h. The supernatants were analyzed for the production of hyaluronic acid using the ELISA assay kit. Results are expressed as means±standard deviations of three independent experiments.
키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단(Nanogel) 은 300 μg/mL, 후코이단 은 1,000 μg/mL 이상의 농도에서 세포 생존율이 100% 기준에서 감소하였으나, 모든 시험군이 80% 이상 생존율로 안정한 군에 속하였다. 85-87%의 생존율을 보인 원료가 안정한 범위에 속하는 것으로 고려하였을 때 안정한 것으로 확인하였다(Kim et al., 2023).
2) 세포 hyaluronic acid (HA) 생성량
Control군에서는 102.67 ng/mL의 시료를 30, 50, 100, 200 μg/mL의 농도로 24 h 동안 처리한 결과, 대조군은 102.67, 109.05, 126.99, 120.03, 121.47 ng/mL, 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단(Nanogel)은 124.09, 188.63, 192.44, 194.87 ng/mL 후코이단이 104.16, 126.31, 154.87, 139.79 ng/mL의 HA의 생성 효능을 보였다(Figure 3B). 인간각질형성세포에서 HA 단백질의 생성이 증가되는 것을 HA에 대한 효소결합면역흡착법 사용 결과로 생성량을 확인한 결과는 보습 효능이 있음을 확인하였다(Shim, 2018).
키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단(Nanogel)이 같은 농도로 처리 하였을 때 모두 HA 생성량이 가장 높게 나타난 것을 확인 하였다.
4. 안티에이징 화장품 개발
1) CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)의 화장품 원료화
2008년 화장품 성분명 표준화 위원회를 시작으로 화장품법 제 12조 및 동법 시행규칙 제 21조 제2호에 의거하여 대한화장품협회를 통해 국내 화장품 성분사전을 통해 화장품 상품명을 등재 하였다(Table 1).
2) MARINAVI-FD를 함유한 안티에이징 화장품 제조
CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)은 MARINAVI-FD 에 스킨 제형 0.5-2.0 % 이내, 크림 제형은 0.8-2.5%로 포함되어 있으며 기초 화장품의 제형에 목적에 맞게 적정량을 쓰는 것을 목적으로 한다. 대표적인 스킨(미스트), 크림의 조성물은 아래와 같다(Table 2).
3) 안티에이징 화장품의 안정성 평가
온도의 조건 4℃, 25℃, 45℃, 60℃에서 1주, 2주, 4주, 12주 기간으로 pH의 변화와 분리 및 침전, 변색, 변취를 확인한 결과 스킨, 크림 모두 제형상 문제가 없었고 물리적 성상에 이상이 없음을 확인하였다(Figure 4). 12주를 보관하여 분리 및 침전, 변색, 변취를 측정한 결과는 화장품의 품질을 위한 안정한 결과를 입증한다(Park et al., 2019). pH의 안정한 제형의 변화 범위는 ±1.0으로 정하였고 시험이 끝나고 스킨, 크림 모두 범위 내에서 안정함을 확인 하였다(Table 3). 나노 입자로 만드는 과정과 제형의 안정화 공정을 감안하여 다층유화기술을 제형에 적용하였기에 가능한 결과이다(Kim et al., 2019). 또한 CD 포접 복합체는 외부적인 요인으로부터 보호받을 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 산소, 열 빛에 대한 안정성이 강화되고 수용해도를 증가 시킬 수 있음을 시사한다(Lee et al., 2019).
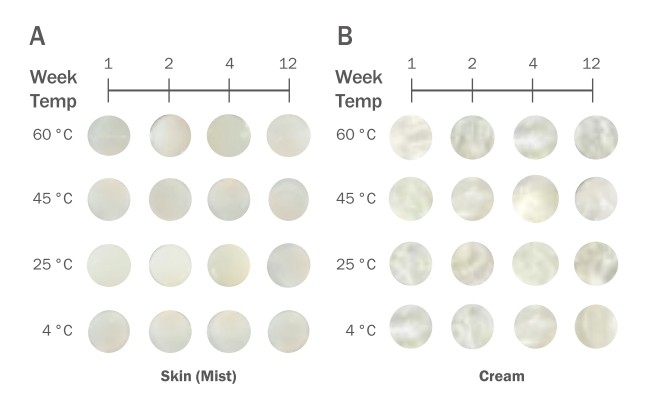
Results of the stability assessment at 4℃, 25℃, 45℃, and 60℃ during the 12-week storage of skin cream containing MARINAVI-FD 1%–3%.
(A) If the pH of the skin (mist) formula had changed, check for precipitation, discoloration, and separation. (B) If the pH of the cream formulation has changed, check for precipitation, discoloration, and separation.
5. 인체적용시험을 토한 피부 2.5 mm 보습 효과
22명의 시험 대상자에게 안면부 왼편에는 단순 후코이단이 함유된 Marinavi-Basic (마리나비 베이직)을 오른편에는 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단(Nanogel)을 포함한 Marinavi-FD (마리나비-에프디)의 시험 제품을 사용전, 사용 2주 및 4주 후 피부 2.5 mm 보습을 측정한 결과는 다음과 같다(Table 4). 정규성 검정에 따라 모수적 방법인 Repeated measures ANOVA로 확인한 결과, 2.5 mm 보습 값은 사용전과 비교하여 사용 2주, 4주 후에 통계학적으로 유의하게 증가하였다. 4주 사용 후 Marinavi-Basic (마리나비 베이직)에 비해 변화가 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단(Nanogel)을 포함한 Marinavi-FD (마리 나비-에프디)의 변화율이 더 크게 나타난 것으로 보이며 나노 입자가 함유된 Marinavi-FD는 항노화의 주요 원인인 피부 건조증에 도움이 될 수 있는 항산화, 보습 효능을 가지고 있는 기능성 화장품 소재이며 모든 화장품 제형에 적합할 것으로 사료되며 키토산/감마-사이클로덱스트린/후코이단(Nanogel) 나노입자는 새로운 피부 후코이단 전달체 소재로 기대할 수 있다. 피부 구조의 표피의 두께는 약 0.1 mm이고 대략 2.5 mm 깊이는 진피층이 위치해 있는데 사용한 후 보습 개선 효과가 나타났고 Marinavi-FD에 포함된 키토산/감마 사이클로 덱스트린/후코이단 (Nanogel)의 영향이 있을 것이라고 사료된다. 인체적용시험을 통한 개선 효과 분석 결과에 따라 기능성 원료로 사용될 수 있는 적합성을 증명할 수 있다(Kim et al.,2023).
Conclusion
본 연구에서는 감마사이클로덱스트린/키토산/후코이단 나노입자(CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel))에 대해 입자 사이즈와 분포도를 확인하였고 피부 유용성 성분의 전달체로서 가능한 범위의 500 nm의 사이즈 부근을 확인할 수 있었다. 나노입자화 하지 않는 후코이단과 비교하였을 때 CH-γ-CD-Fu (Nanogel)이 항산화와 보습 효능을 보았고, 이 나노입자를 포함한 MARINAVI-FD를 화장품 소재화 하여 스킨과 크림 제형의 안정성을 확인하였다. 또한 인체적용시험을 통해 피부 2.5 mm 보습 개선 효과에 도움을 주는 소재인 것을 증명하였다. 정상 피부는 가장 외부 얇은 표피층은 0.05 mm-1mm 두께를 가지며 진피에 도달하는 평균적인 피부 두께는 1-2 mm 정도라고 하였을 때 2.5 mm에 보습 효능 나노 입자가 도달하였을 때 경피 약물 전달 시스템(TDDS)의 새로운 피부 전달체로 피부 노화 방지와 피부 장벽 개선 등의 유효성을 가진 피부 전달체의 소재로 활용이 가능할 것으로 기대된다. 또한 피부에 나노입자의 흡수율을 높여 줄 수 있는 저주파, 고주파, 미세전류, 온도센서, LED 등의 미용기기와의 융합 시너지 효과를 기대해볼 수 있다. 추후에 원료의 사업화를 위해서는 대량 공정에 따른 후코이단 추출 후 순도 및 분자량 조절 연구가 더 필요하며 보완 연구가 이루어 진다면 MARINAVI-FD의 국내 및 해외의 화장품 원료 시장의 활용이 가능 할 수 있음을 시사한다.
Acknowledgements
본 연구는 2022년도 중소벤처기업부의 창업성장기술개발사업디딤돌 지원에 의한 연구임[S3290537].
Notes
Author's contribution
D.I.C. and S.Y.L designed all experimental investigations, and S.M.P developed the process for cosmetic developmenting the ingredient. M.K.J collected data.
Author details
Da-In Choi (Research Professor), mart Medical Convergence Technology Support Center, Chosun University, 208 Cheomdangwagi-ro, Buk-fu, Gwangju, Korea; Min-Kyeong Ju (Team Leader), Corporate Research Institute, Innoflux Ltd., 220, Myeongsasimni, 61beongil Sinji-myeon, Wando-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea; Su-Mi Park (Chief Executive Officer), Corporate Research Institute, Innoflux Ltd., 220, Myeongsasimni, 61beon-gil Sinji-myeon, Wando-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea; Sook-Young Lee (Professor), Marine Bio Research Center, Chosun University, 61-220 Myeongsasimni, Sinji-myeon, Wandogun 59146, Jeollanam-do, Korea.